Introduction
Google Cloud Document AI API and Google Cloud Vision API are both Google Cloud services designed for processing documents and images.
1.Document Processing:
- Document AI API:
Document AI API focuses on processing structured documents, such as PDFs and OCR
documents. Its primary functionalities include text extraction, table recognition
page identification, entity recognition (e.g., identifying dates and amounts in
contracts), and more. This makes it suitable for handling business documents like
contracts, invoices, reports, and others.
- Vision API:
Vision API specializes in processing images and pictures. It can recognize
objects, faces, scenes, text, and more within images. Its main applications
include image classification, facial recognition, OCR text recognition, and more.
This makes it suitable for image processing applications like image search, facial
recognition, and automated image analysis.
2.Application Scenario:
- Document AI API:
The Document AI API is suitable for business scenarios that involve processing a
large volume of structured documents, such as contracts, invoices, and medical
records.
- Vision API:
The Vision API is well-suited for applications that require processing images and
photos, such as image analysis and image search.
Code Demo
☁️ Cloud Vision
- Recognize text in pictures
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #Detect online images
from google.cloud import vision
def detect_document_text_uri(uri):
"""Detects document text in the file located in Google Cloud Storage or on the Web."""
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
image = vision.Image()
image.source.image_uri = uri
response = client.document_text_detection(image=image)
document = response.full_text_annotation
print(document.text)
if response.error.message:
raise Exception(
"{}\nFor more info on error messages, check: "
"https://cloud.google.com/apis/design/errors".format(response.error.message)
)
detect_document_text_uri('https://i.redd.it/2aby2h2mhtpb1.jpg')
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #Detect local images
def detect_text(path):
"""Detects text in the file."""
from google.cloud import vision
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
with open(path, "rb") as image_file:
content = image_file.read()
image = vision.Image(content=content)
response = client.text_detection(image=image)
texts = response.text_annotations
if texts:
print(texts[0].description)
detect_text("profile path")
|
Click ▶ to expand the examples
Example & Result (online images)

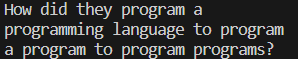
Example & Result (local images)

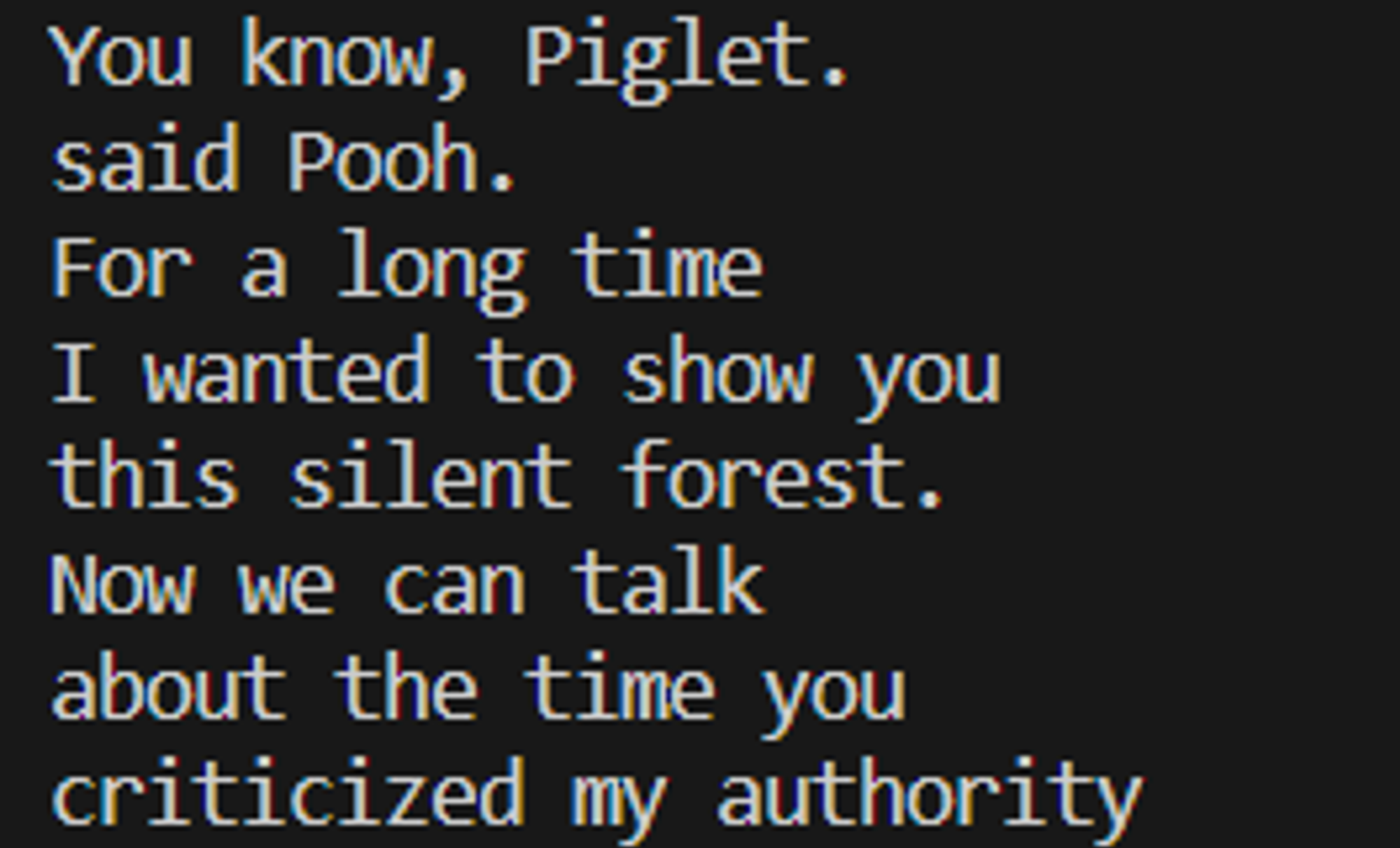
- Recognize handwriting in pictures
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #Detect text in online images
def detect_document_uri(uri):
"""Detects document features in the file located at the given URL."""
from google.cloud import vision_v1
client = vision_v1.ImageAnnotatorClient()
image = vision_v1.Image()
image.source.image_uri = uri
response = client.document_text_detection(image=image)
for page in response.full_text_annotation.pages:
for block in page.blocks:
for paragraph in block.paragraphs:
for word in paragraph.words:
word_text = "".join([symbol.text for symbol in word.symbols])
print(word_text)
if response.error.message:
raise Exception(
"{}\nFor more info on error messages, check: "
"https://cloud.google.com/apis/design/errors".format(response.error.message)
)
detect_document_uri('https://ocr-demo.abtosoftware.com/uploads/handwritten3.jpg')
|
Example & Result (local images)


Example & Result (online images)

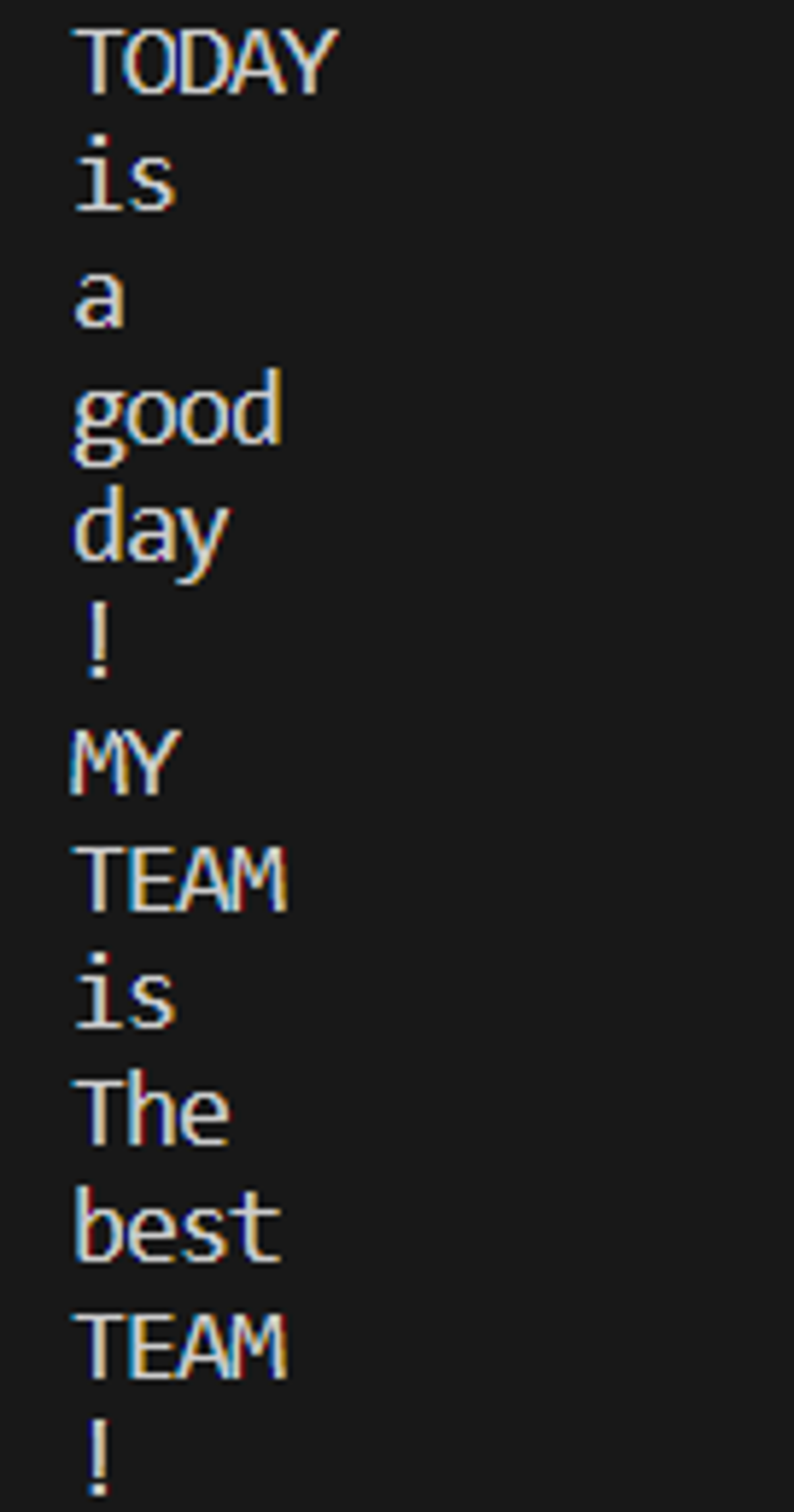
📃 Document AI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| from typing import Optional
from google.api_core.client_options import ClientOptions
from google.cloud import documentai
def process_document_sample() -> None:
# Specify Google Cloud ID & other parameters
project_id = "your project id"
location = "us"
processor_id = "your processor id"
mime_type = "application/pdf"
field_mask = "text,entities,pages.pageNumber"
processor_version_id = None # Do not use a specific processor version
#Input file path
file_path = input("Please enter the path to the PDF file you want to process: ")
# Initialize Document AI client
client = documentai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient()
if processor_version_id:
name = client.processor_version_path(
project=project_id, location=location, processor=processor_id, processor_version=processor_version_id
)
else:
name = client.processor_path(project=project_id, location=location, processor=processor_id)
with open(file_path, "rb") as image:
image_content = image.read()
raw_document = documentai.RawDocument(content=image_content, mime_type=mime_type)
request = documentai.ProcessRequest(
name=name,
raw_document=raw_document,
field_mask=field_mask
)
result = client.process_document(request=request)
document = result.document
print(document.text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
process_document_sample()
|
Through exploring these APIs, I learned about their
specific applications in handling structured documents and images, and the
potential for automating tasks in business and image analysis contexts.
Looking ahead, these insights could be applied in developing more efficient
document management systems, enhancing data extraction from documents, and
improving image-based search and analysis in various industries.








